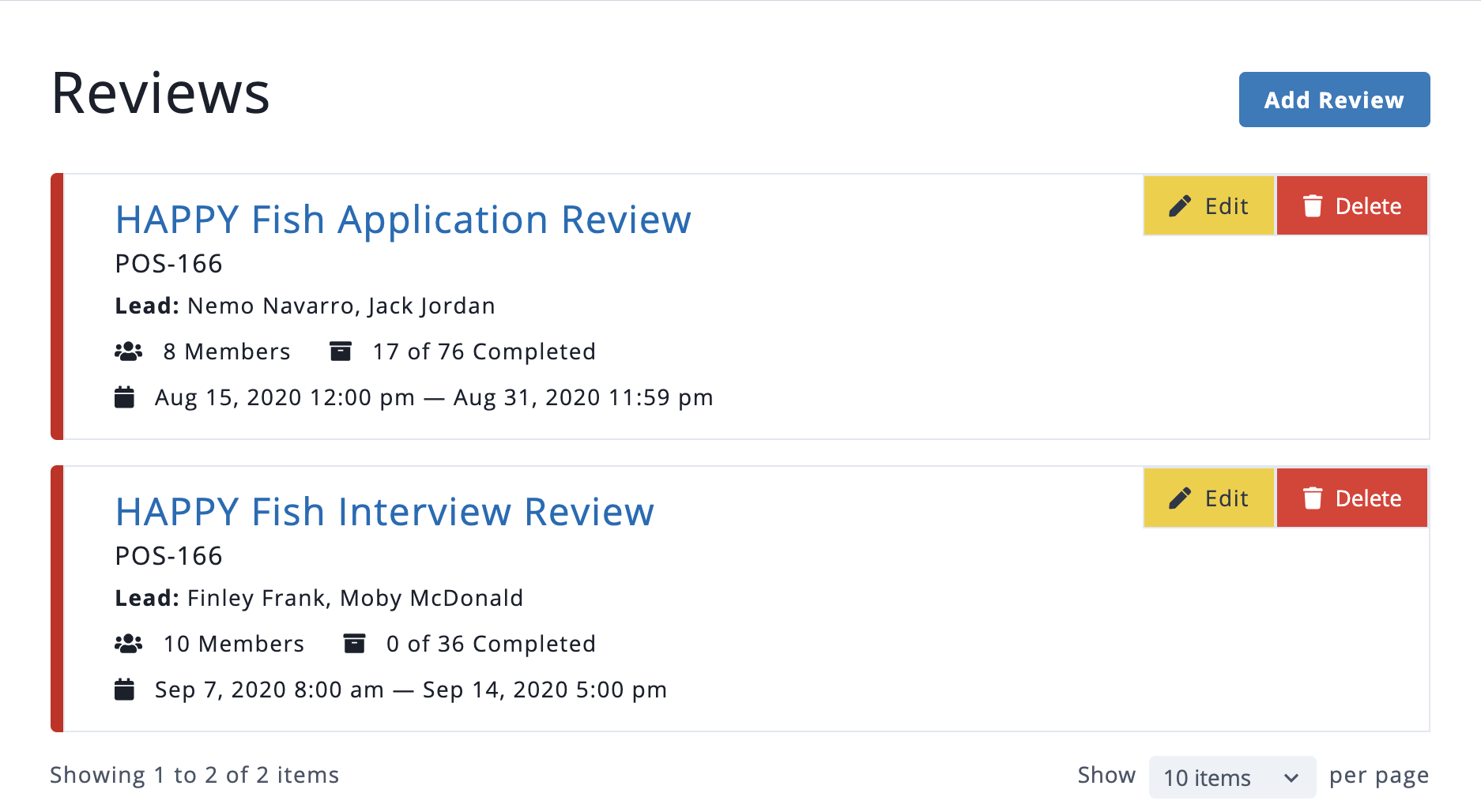
Reviews are the process of evaluating submitted items to decide which items to select or approve. It enables a team of reviewers to view and score the items before reaching a decision.
Here are some possible uses for Reviews (not all of which are yet supported by the Get Involved service):
- Membership applications
- Interview scoring
- Request form submissions
- Award nominations
- Workshop presentation proposals
Note: Multiple Reviews can be associated with the same set of things. For example, applications for an officer position may be reviewed by a primary selection committee and separately by a broader set of stakeholders. This keeps the scores separate in case they should be weighted differently in making a final decision. Similarly, if a pool of applicants may be considered for assignment to one of several subcommittees within an organization, separate Reviews (with different teams of reviewers) can be defined for the same set of applicants.
There are three roles for the review process:
- Lead Reviewer – This type of user can do everything a Reviewer can do and also has administrative permissions to create, manage reviews including designating review team members, designating submitted items to be included in the review process, and monitoring progress by the team, and marking decisions about each item.
- Reviewer – This type of user has no permissions within the administrative module but can view and act on items that are part of the review to which the user is assigned. Depending on the type of review, actions can be to score, decide, aor to provide feedback.
- Viewer – This type of user can only view review items but cannot score, make decisions, or provide feedback. This allows them to be informed by but not act in a review. This type of user has no permissions within the administrative module.
The Status of a Review will be one of three values: Draft, Published or Completed.
Selection Process Overview
This overview describes the process for reviewing membership applications but could be similarly applied to other types of review.
- Configure a Position to accept submissions of membership applications – Currently, workflow configuration requires the assistance of IT.
- Sequence the application sections – The different forms and agreements that composed an entire application packet can each be shown in a particular sequence or hidden from the reviewer’s view. This allows sections with personally identifying information to be hidden from blind selection processes and hides electronic signatures for agreements that are equally required of every applicant since that information adds no value to making a selection decision. The sequence of the sections that are to remain visible to reviewers can be specified to provide a consistent presentation of all applications. Currently, sequencing requires the assistance of IT.
- Create a Review associated with the Position – There are three possible types of decision methods:
- Rubric Scoring – This method lets you have one or more reviewers use a weighted rubric to score each item. The average scores can be used to rank the items to decide which items will ultimately be accepted or rejected.
- Configuration options include specifying the minimum number of reviewers for each item (not requiring every review team member to score every submission is especially helpful for large numbers of submissions).
- One or more questions can be configured with the range of possible numeric scores (e.g. 0-5, 1-10). Questions can be weighted differently if desired (a question having a maximum possible score of 10 is weighted twice that of a question with a maximum possible score of 5).
- Straight to Decision – This method lets one person make an instant decision to accept or deny an application or proposal.
- Feedback – This method lets one or more reviewers provide feedback without a final decision. Feedback can include a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” reaction and/or comments that can be viewed by others, including to inform them as they make a final decision. The reaction is not treated the same as a decision and may be changed repeatedly with submission of additional comments as iterative feedback.
- Rubric Scoring – This method lets you have one or more reviewers use a weighted rubric to score each item. The average scores can be used to rank the items to decide which items will ultimately be accepted or rejected.
- Identify team members – Reviewers will be able to view relevant application materials and submit a score for each set. Be sure to train them on how to apply the rubric so scores will be normalized. Lead Reviewers can configure the review and track progress of the review process.
- Add submitted items to the Review – Submitted items are not automatically added for consideration. This lets a Lead Reviewer screen the applications to ensure prerequisite qualifications are met and to prevent improper items from being passed on to review team members.
- Monitor the scoring progress – Many factors can be tracked throughout the process including the number of items that have been completely scored and the number the items a team member has chosen to skip.
- Make acceptance decisions – Each item being scored can be tagged as Accepted, Declined or Undecided. This decision can inform the next step in the selection process. For example, submitted applications that “make the cut” can be invited to interview. Those approved in a first round of interviews can be approved to advance to a second round of interviews. Those accepted after the second round can be accepted as active members of the organization.

